-
-
Like what you see?
LetsTalkUrl
Let's Talk
From using data to improve user safety to delivering personalized services anytime, anywhere and through any channel, new technologies enable motor vehicle and licensing agencies to digitize operations and service delivery.
Digitization means use of technology to transform business processes and support the introduction of innovative customer goods and services. One example is digital credentials.
Digital credentials are electronic versions of the driver license, vehicle registration, learners permit, temporary trip permits or any other document that the DMV issues a customer. These credentials offer a digital, secure and a convenient way for customers to access various DMV services.
Static digital credentials are already in use today in the form of downloadable or printable PDFs. They do not require real time access or updates and usually have a single purpose.
For example, customers may be able to download, print and retain their vehicle registration from the DMV website. The data on the registration is stored with the DMV, and actions against that data require an in-person activity or transaction.
Dynamic digital credentials are interactive and reflect updates performed by either the customer or the DMV in real-time. One example is the change of address by a customer. Once verified, the change of address will be updated to the digitized credential, like a vehicle registration or driver’s license. Another example is an action against the driver taken by the DMV. In this case a license suspension, revocation, reinstatement or similar enforcement action can be uploaded to the digitized credential in real or near-real time. These updates would be immediately available for display when a digital registration or driver license is accessed by the customer or law enforcement.
Digital credentials enable jurisdictions to develop a secure workflow, allowing customers to perform transactions online through their preferred channel and device.
A great deal of work has already been done on the digital license front, specifically the Mobile Driver License (MDL). Several jurisdictions have piloted the MDL. There are other possible applications for digital credentials beyond the MDL. Learner’s permits could follow the same progression as the digital driver’s license. Digitized or electronic titles and vehicle registration can be as impactful as MDLs, especially from a commercial perspective, like IRP.
If a commercial vehicle has to add route and mileage while it is in transit, then the home office can perform the transaction and upon completion, the digitized credential residing in the driver’s tablet would be automatically updated. This could also link to additional IFTA payments. The vehicle can now proceed on its new route without disruption and the updated IRP credential will be available for review at roadside weigh stations or other inspection points.
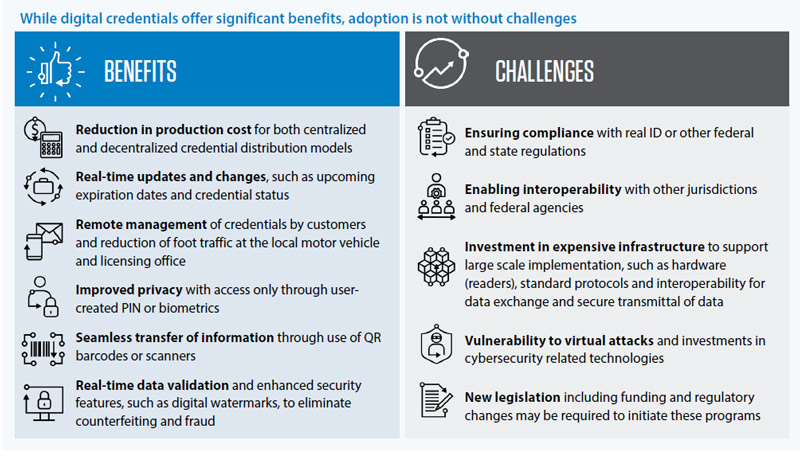
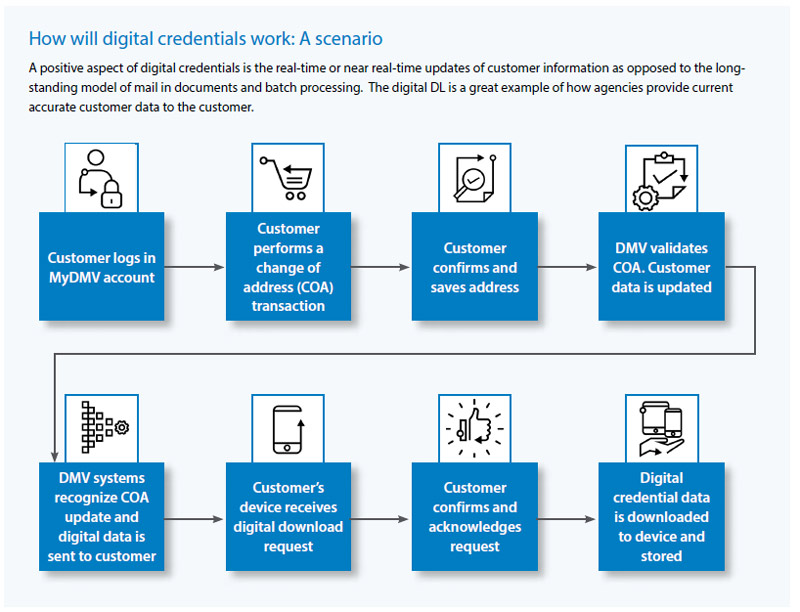
For agencies to be successful in digitizing credentials, they must embrace a digital journey, not just in terms of customer expectations, but also in the larger expectations of state services, of state staff and the entire cross agency business environment. Here’s how agencies can start their digital credentials journey:
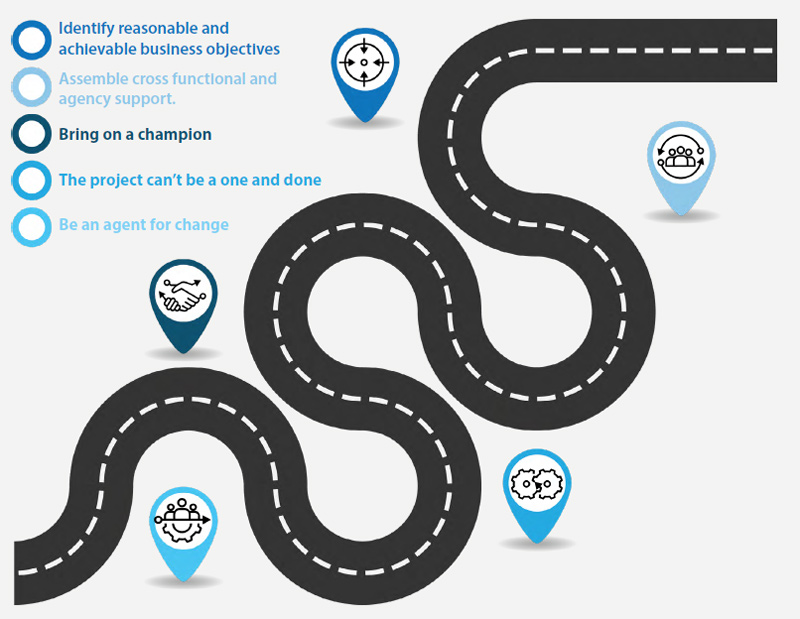
Successful digital transformation helps develop reusable technical infrastructure that can be employed by all agencies, providing a common look and feel (branding), lowering cost through sharing infrastructure and improving time to market through repeatable process improvement.
The next few years will witness digital credentials becoming a key component of jurisdictions’ digital transformation journey. While digital credentials offer many benefits, jurisdictions should ensure they remain secure and can be easily processed by the various partner agencies and jurisdictions they work with. The approach outlined above can help jurisdictions successfully navigate their digital credential adoption journey.