Transforming Social Services: How a State HHS Agency Modernized and Enhanced its Integrated Eligibility System
About the Client
A Northeastern State Health and Human Services Agency that administers 90+ social programs, including Medicaid, Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), and Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) to over 3.5 million residents.
Situation
The agency operates and maintains several applications, including the ones outlined in Table 1, as part of its Integrated Eligibility system to administer social programs. These applications are primarily managed by four departments and offices within the agency:
- The Social Services department is responsible for managing the business operations of applications for robotic process automation, long-term care, public-facing services, and the case worker portal.
- The Early Childhood department manages modules within the public-facing and case worker benefits portal related to early childhood benefits programs such as Head Start and state-funded early care and education programs.
- The HIX Office oversees the State’s insurance marketplace, including the HIX Application.
- The IT Department provides IT support and services for the entire agency.
Key challenges
The agency encountered several issues while managing these applications, from high operational costs and increased administrative burden on case workers to a diminished citizen experience and non-compliance with federal and state policies.
| Application | Functionality | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Robotic Process automation |
|
|
| Long-Term Care Application |
|
|
| Public-Facing Benefits Portal |
|
|
| Case Worker Benefits Portal |
|
|
| Health Insurance Exchange (HIX) Application |
|
|
The Solution
Infosys Public Services assisted the agency in transitioning its system from its initial state, characterized by elevated expenses and quality challenges, to a desired future state. Enhanced communication and collaboration, cost-efficient maintenance, streamlined development processes, high availability, and an ongoing commitment to continuous improvement marked this evolution.
Utilizing its established transition methodology, the Infosys Transition Advantage (ITA), Infosys Public Services successfully transitioned all five Integrated Eligibility System (IES) applications from the incumbent vendor. This was achieved despite encountering resistance and insufficient documentation from the previous vendor. The comprehensive transition process was finalized within 15 months and consisted of an initial transition planning phase followed by three sequential transition waves, as detailed in Figure 1 below.
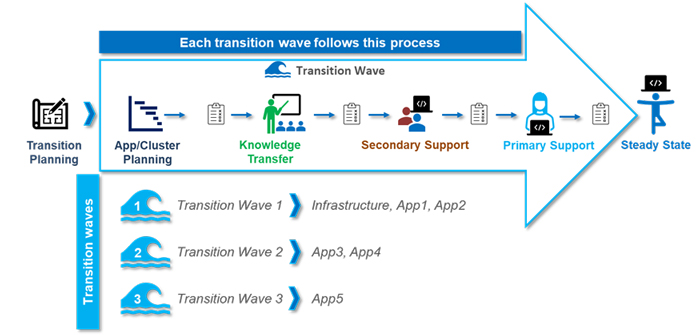
As Infosys Public Services navigated the transition, it managed and maintained applications across all five areas, delivering exceptional support in application monitoring, incident management, problem management, and batch monitoring tasks.
During the initial transition planning stage, Infosys Public Services collaborated with the previous vendor, the client, and other contractor teams in the IES ecosystem to perform onboarding, due diligence, and planning activities. The team validated the scope, implemented transition tools and processes, established success criteria and governance, created a knowledge acquisition plan, aligned the team, and initiated network connectivity.
In the first wave, Infosys Public Services prioritized infrastructure, RPA (App1), and Long-Term Care applications (App2). By focusing on these applications, the team was able to address the business and IT requirements of the State’s Social Services and IT departments. The team successfully resolved various AWS infrastructure issues and implemented an efficient RPA bot optimization, reducing wait times and costs. Additionally, the team utilized Equifax API to expedite case processing for the Long-Term Care Application.
Infosys Public Services used the knowledge gained from the first two phases when they took on the remaining applications in the following phases. The team collaborated with State teams to oversee the public-facing benefits portal (App3), case worker portal (App4), and health insurance exchange applications (App5).
In the steady-state phase, the team focused on continuous improvement and value realization. The team is implementing several interventions, including but not limited to:
- Lean Practices: Day in the Life Of (DILO) analysis, Skill Heat Map analysis, and Pyramid Optimizer (POT) analysis to optimize task allocation and improve productivity.
- Automation: Query Optimization, implementation of New Relic monitoring, and newly created automation tools to expand the scope of automation.
Benefits
The agency was able to realize several benefits through the program.
- Significantly lower cost of operations across the five different systems
- Improved case worker productivity through optimization of processes and automation
- Compliance with federal and state policies
- 99% system availability for the Case Worker Benefits Portal

