-
-
Like what you see?
LetsTalkUrl
Let's Talk
In the contemporary digital landscape, public services are increasingly reliant on robust and reliable IT infrastructures to deliver seamless experiences to citizens. Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) provides a methodological approach that guarantees the high availability, scalability, and performance of essential systems.
The primary objective of SRE is to develop systems that are both scalable and reliable, achieved through the automation of tasks, management of incidents, and assurance of service availability, performance, and efficiency. SRE acts as an intermediary between development and operations teams, with the aim of enhancing system resilience and improving the overall user experience.
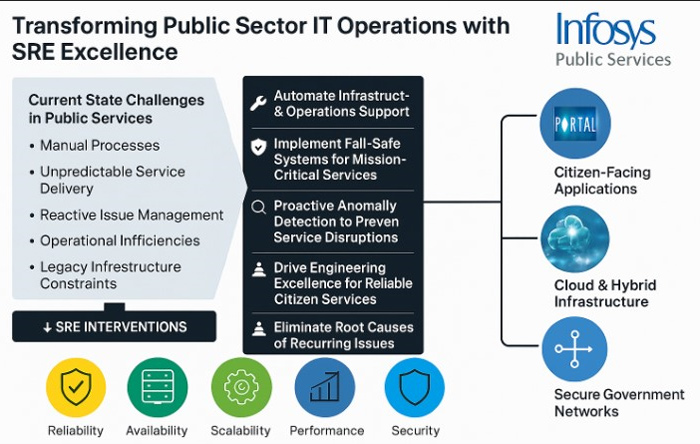
While Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) holds immense potential, traditional approaches often fall short in meeting the unique needs of public sector organizations. These limitations hinder effective adoption and impact. This blog delves into the specific gaps in conventional SRE practices and introduces a modernized framework designed to help public sector teams implement SRE more effectively and sustainably.
Analysts increasingly recognize Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) as a strategic imperative for modern enterprises. According to Gartner’s 2025 Hype Cycle for SRE, the discipline has evolved beyond ensuring system reliability to becoming a catalyst for innovation. The report highlights how AI agents and large language models (LLMs) are revolutionizing incident response and root-cause analysis, while continuous resilience automation and OpenSLO standards are helping organizations balance risk with development velocity. Gartner forecasts that by 2028, 80% of enterprises will adopt SRE practices to enhance product design, reduce costs, and streamline operations.
Complementing this, Atlassian’s research across 145 organizations reveals that structured SRE adoption leads to a 47% increase in system reliability and a 32% reduction in Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR), with a strong correlation between SRE maturity and operational efficiency. Sector-specific insights show significant gains in financial services, technology, and healthcare, positioning SRE as a transformative force in regulated and high-availability environments.
Traditional SRE approaches often lack a comprehensive, structured framework, leading to fragmented processes, inconsistent application of principles, and a limited ability to scale effectively across an organization. They often lack clear, quantitative goals and a direct link to business outcomes.
Infosys plugs these gaps with a structured, data-driven methodology that includes:
Infosys Public Services adopts a structured methodology for SRE implementation, focusing on key pillars such as automation, observability, and incident response. This approach includes:
1. Balancing Manual and Automated Processes: While automation is key, there are times when manual intervention is necessary. This includes diagnosing unexpected issues, overseeing critical incidents, and implementing immediate fixes to maintain service availability.
2. Unpredictable vs. Predictable Events: The nature of technology means that issues can arise unexpectedly. We train SRE to handle these unpredictable events, employing strategies that allow them to quickly stabilize systems and minimize downtime.
3. Fire Fighting: This refers to the urgent need to address critical incidents that arise unexpectedly. SRE teams equip themselves with incident response protocols to effectively "fight fires" when they occur, ensuring that services are restored as quickly as possible.
4. Optimizing Systems: Beyond just maintaining systems, SRE is dedicated to continuous improvement. This includes fine-tuning services and infrastructures to achieve better performance and utilize resources more effectively.
5. Inefficiency Reduction: SRE practices aim to identify and eliminate inefficiencies in processes, workflows, and systems. By streamlining operations, teams can enhance reliability and performance.
6. Performance Monitoring: Achieving high performance is a primary goal of SRE. This involves continuous monitoring of systems to ensure they operate within the desired parameters and meet user expectations.
7. SRE Culture: Cultivating an SRE culture within organizations fosters collaboration between development and operations teams. This shared responsibility ensures that reliability is prioritized at every level, promoting a culture of accountability and innovation.
Implementing these SRE practices enhances system resilience and operational excellence. Automation in infrastructure and operations helps identify anomalies early, reducing downtime. Engineering excellence ensures a balance between reliability and innovation. Optimizing costs, workflows, and performance through streamlined processes increases efficiency. Proactive analysis addresses root causes to improve stability. Continuous learning fosters quick adaptation to technological changes and promotes proactive incident management. Prioritizing automation and cost savings aligns with resilience goals, supporting sustainable growth and better customer value.
The structured approach to implementing the SRE function begins with assessing the existing adoption ecosystem and understanding the application portfolio characteristics. Key steps include defining high-level adoption goals, scope, and team structures, as well as identifying essential tools.
Implementation involves establishing SRE capabilities, setting up SLO (Service Level Objectives) and SLI (Service Level Indicators) tracking mechanisms, and conducting periodic reviews of application portfolio performance.
Continuous improvement is achieved through ongoing optimization and organizational change management. Additionally, defining the SRE to-be state, determining error budgets, and clarifying team structures are crucial for successful deployment and sustaining reliable service delivery.
The SRE Adoption Ecosystem constitutes a comprehensive framework encompassing the essential components of personnel, processes, and technology required for the successful implementation of Site Reliability Engineering (SRE). This framework emphasizes a cultural transformation, the establishment of well-defined metrics, and the utilization of automation to create resilient systems. Key considerations for SRE adoption include:
SRE principles are universally applicable regardless of application or portfolio characteristics. The SRE Operating Model can be tailored based on the specific attributes of the application or portfolio, considering existing support structures and the flexibility to modify them.
Regardless of the scope of direct implementation, SRE teams are responsible for achieving Service Level Objectives (SLOs) by monitoring variables affecting service levels end-to-end.
The effectiveness of SRE can be influenced by cross-team interactions; therefore, minimizing handovers and dependencies, coupled with strong governance, is essential. Additionally, the operating model should be reviewed periodically to adapt to evolving application and portfolio characteristics.
1. Automation-Driven Efficiency
Infosys leverages automation pipelines to streamline routine tasks, reduce manual effort, and enhance operational efficiency across public sector services.
2. Proactive Monitoring and Incident Management
Real-time alerting and structured incident workflows ensure rapid detection and resolution of issues, minimizing service disruptions and citizen impact.
3. Seamless Integration with Legacy Systems
The SRE framework is designed to integrate smoothly with existing public sector IT infrastructure, including cloud platforms, ensuring minimal disruption.
4. Scalable and Resilient Architecture
Infosys enables dynamic scaling and resilient system design to maintain service continuity during peak loads and adverse conditions.
5. Cost Optimization and Resource Utilization
Through automation and intelligent resource allocation, Infosys helps public agencies reduce operational costs while maintaining high service quality.
6. Change Management and Team Enablement
Infosys supports SRE adoption with tailored roadmaps, training programs, and a culture of reliability to empower public sector teams for sustainable transformation.
As public services continue to embrace digital transformation, the need for resilient, scalable, and citizen-centric IT operations has never been greater. Infosys Public Services’ Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) offerings empower government agencies to move beyond reactive maintenance toward proactive innovation. By integrating automation, observability, and a culture of reliability, public sector organizations can unlock new levels of operational excellence and service continuity.
With a structured roadmap, proven frameworks, and deep domain expertise, Infosys enables agencies to not only meet today’s reliability demands but also future-proof their systems for tomorrow’s challenges. The journey to sustainable, high-performing public services starts with SRE—and Infosys is ready to lead the way.

Ajay Kumar is a seasoned technology leader with over 24 years of experience driving large-scale digital transformation initiatives, from initial project implementation to final system integration and enterprise architecture. As principal Technology Architect at Infosys Public Services, he leads the Cloud and Infrastructure practice and is instrumental in helping clients modernize their technology landscapes.
Ajay is known for his strategic vision and collaborative leadership. Ajay excels at aligning complex business objectives with innovative technical solutions. He has a proven track record of spearheading programs that leverage agile methodologies, digital experience platforms, and cloud technologies to foster business innovation.
He is passionate about mentoring and guiding teams, actively sharing his insights on emerging technology trends to build a culture of continuous learning and excellence.